Cost of Capital
Meaning of Cost of Capital
Capital is the money that is required for business day-to-day operation and future growth. There are mainly four types of shareholder's capital includes common stock, preferred stocks, debt capital (bonds and debentures) and retained earnings.
Cost of capital is the weighted average cost of various sources of fund like equity and debt. It is the minimum rate of return that a company expects to earn from its investment in order to maximize the value of the firm in the market.
Components of Cost of Capital
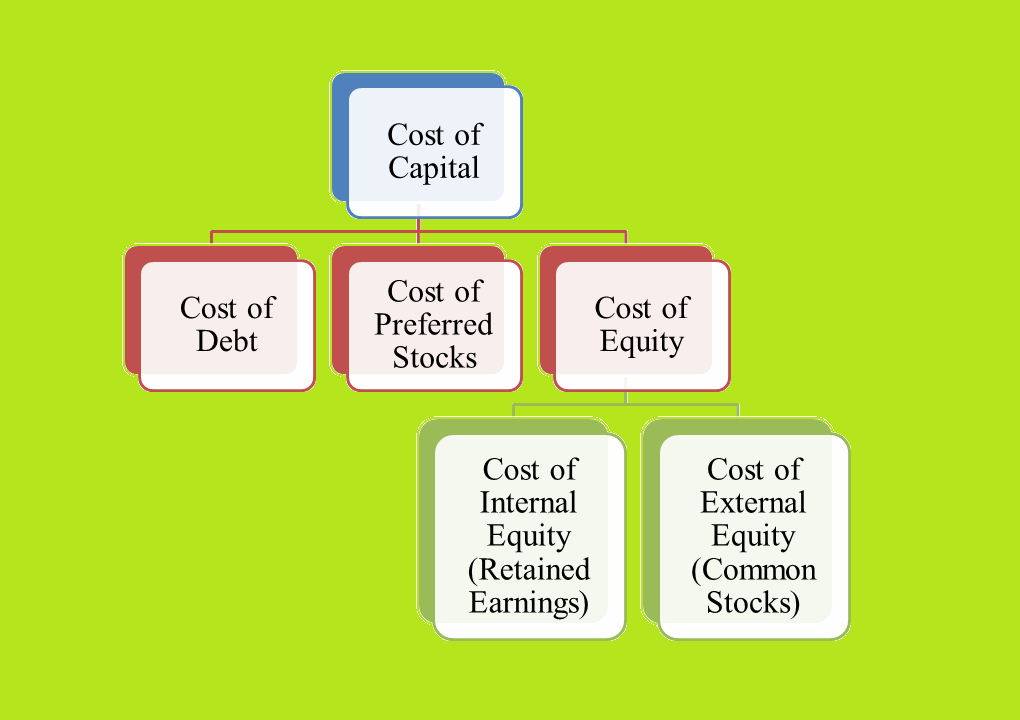
Generally, there are three types of financing used by the firm include debt, preferred stock and equity. The equity further two types includes internal equity (common stock) and external equity (retained earnings). So based on these sources of fund, there are mainly four components comes for calculating cost of capital of the firm described as bellows:
Cost of Debt (Kdt): It is the effective interest rate that a company is paid on its debts. It can refers to before tax rate which is the cost of company's debt before considering the tax. The cost of debt must be evaluated by adjusting the tax rate i.e. calculated the rate in after tax.
Cost of Preferred Stock (Kps): It is the rate of return required by preference shareholders. It can be calculated by dividing the annual DPS on current market price.
Cost of External Equity/Common Stock (Ke): It is the minimum rate of return that an investor must earn due to the reasons of considering risk-free rate and risk premium.
Cost of Internal Equity/Retained Earnings (Ks): It is an opportunity cost for the company that is internally generated.
Fig: Classifications of Cost of Capital
Note: Cost of debt should be
calculated in after tax by using this way:
Kdt = kd*(1-t).
Concept of WACC
The WACC stands for weighted average cost of capital. It is the tool that helps to determine the minimum required rate of return for break even. It is an discount rate that a company used to calculate Net present Value (NPV). It is important to analyze company's financial health. Lower the WACC good financial health while higher the WACC weak financial health of the business. The weighted average cost of capital of a firm is composed of the cost of all long-term sources of capital it uses. It can be calculated by using the following steps listed as bellows:
Calculating the cost of each sources of capital
Identifying the weight of each sources of capital
Multiplying the cost with weight of each sources of capital
Summing the product of each sources of capital
The formula for WACC
The WACC can be calculated by using the following formula as bellows:
WACC = [Wd*Kdt]+[Wps*Kps]+[We*Ke]+[Ws*Ks]
Where,
Wd = Weight of debts
Wps = Weight of preferred stock
We = Weight of common stock
Ws = Weight of retained earnings
Kdt = Cost of Debt in after tax
Kps = Cost of preferred stocks
Ke = Cost of equity
Ks = Cost of retained earnings
Cost of Sources of Funds
There are various formulas and models to calculate the cost of various sources of funds. All the sources of funds are classified into four categories having different formulas and models presented in the table below:
Table: Formula for Calculation Cost of Fund
Yield to Maturity (YTM): It is a formula that is basically used for calculating the cost of debts sources of fund. It is the total rate of return that a bond or debenture earned. It is important to adhere the mode of interest payment on bond or debenture while calculating YTM. It is calculated to determine the price of bond on three basis as premium, discount and fairly bond. It the YTM is less than bond's coupon rate, then is said as premium bond. Similarly if the YTM is greater than bond's coupon rate, then it is said as discount bond otherwise fairly bond.
Dividend Discount Model (DDM): It is the quantitative methods to predict the value of equity or stocks based on current market and expected dividend per shares. It is important to adhere the DPS and time period estimation while using this model.It is calculated to compare the price of stock on three basis as overpriced, under-pried and correctly priced. It the value of stock is less than current price of stock, then is said as overpriced stock. Similarly if the value of stock is greater than current price of stock, then it is said as under-priced stock otherwise fairly priced stock.
Capital Assets Pricing Model (CAPM): It is the methods that helps to determined the required or expected rate of return on stocks. It shows the linear relationship between required rate of return and systematic risk.
Note: Assume 4% always for risk premium in risk premium method.
Cost of capital is the weighted average cost of various sources of fund like equity and debt. It is the minimum rate of return that a company expects to earn from its investment in order to maximize the value of the firm in the market. Generally, there are three types of financing used by the firm include debt, preferred stock and equity. The equity further two types includes internal equity (common stock) and external equity (retained earnings). There are mainly four components comes for calculating cost of capital includes cost of debt, cost of preferred stock, cost of equity and cost of retained earnings. There are four steps to calculate WACC includes calculating the cost of each sources of capital, identifying the weight of each sources of capital, multiplying the cost with weight of each sources of capital and summing the product of each sources of capital. Cost of equity and retained earnings can be calculated by using CAPM and DDM. The cost of preferred stock can be calculated by using DDM and cost of debt can be calculated by using YTM (Yield to Maturity).
Come On, Tell Me What You Think!
Did I miss something? Come on! Tell me what you think about this post on Cost of Capital in the comments section.




Comments
Post a Comment
If you've any doubts or suggestions please let me know.